It’s the lag time.
To no one’s surprise, the Federal Reserve continued to battle inflation last week, raising the federal funds rate for the fourth time this year, reported Claire Ballentine of Bloomberg. The Fed is making borrowing more expensive to dampen demand for goods, which should lower inflation – but it’s not a quick fix.
Rate hikes are kind of like winter planting. In cold weather areas, people sometimes spread grass seed in November with the expectation that it will germinate the next spring. It’s similar for rate hikes. The Fed lifts rates with the expectation that the increases will work their way through the economy over the next 12 to 18 months and bring inflation down, reported Matt Levin of MarketPlace.
That lag time can make it difficult for the Fed to know when it has done enough.
Over the last eight months, the Fed’s benchmark rate has increased from near zero to 3.75 percent, reported Nicholas Jasinski of Barron’s. Over that period, inflation, as measured by the Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) Price Index, has moved slightly lower. In March, the headline PCE Price Index was 6.6 percent, year-over-year. In September, it was 6.2 percent. The core PCE Price Index, which excludes food and energy prices, was 5.2 percent in March, year-over-year, and 5.1 percent in September.
Last week’s unemployment report showed the economy remains strong, but there were signs that Fed rate hikes are beginning to have an effect. The rate of new jobs growth slowed even as U.S. businesses reported stronger-than-expected hiring increases, reported Jeff Cox of CNBC. Jobs gains were spread across industries, and average hourly earnings increased. In addition, the number of layoffs rose, although the number remained at historically low levels, according to Augusta Saraiva and Reade Pickert of Bloomberg.
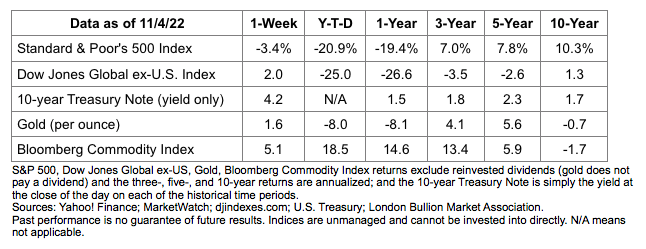
Last week, major U.S. stock indices finished lower. Treasury yields rose across all maturities as investors priced in the expectation that the Fed will keep raising rates into 2023.
Baseball Players Are Superstitious and So Are Investors
The sport of baseball is steeped in superstition. Many players, managers and announcers follow routines and unspoken rules. For example, some say that mentioning the possibility of a no-hitter while it is in progress can jinx the outcome.
In 2020, ESPN’s Tim Kurkjian reported on the routines of retired pitcher Edward Mujica. “He always has to be in the same spot of the bullpen with two outs in the fourth inning of every game. Then, in the fifth inning, he always digs a hole at the front end of the bullpen mound. Then he spits a half cup of red Gatorade into the hole…”
Mujica is not alone. It was rumored that outfielder Torii Hunter cleaned his spikes at exactly 6:40 p.m. before every 7:05 p.m. game, reliever Sean Burnett had a poker chip in his pocket whenever he pitched, and infielder Ryan Zimmerman always used the same shower stall.
Throughout this year’s World Series, we’ve been hearing about another superstition: When the Philadelphia Phillies win the World Series, the U.S. economy tends to slide into recession or the market falls. The Phillies lost over the weekend, and the Astros took home the pennant. Before you breathe a sigh of relief, thinking the Phillies loss will spare the economy and stock markets, check out the data.
From 20,000 feet, the data made for some great clickbait headlines, but when you look closer the facts don’t support the supposition. The Phillies won titles in 1929, 1980 and 2008.
In 1929, the World Series game was played in early October. The recession had begun two months before, in August 1929. That’s when the stock market began to decline, too.
In 1980, the World Series was played in mid-October. The recession had begun in January 1980, and the stock market decline started in February.
In 2008, the World Series was played in late October. The recession had begun the previous year, in December. The stock market decline also began in 2007.
Then, of course, there is the fact that there have been many recessions and market downturns during years the Phillies weren’t in the World Series. It looks like this superstition will have to be benched alongside the Hemline Indicator (the stock market rises and falls with the women’s hemlines), the Pigskin Predictor (when an original NFL team wins the Super Bowl, stocks go up), and the Triple Crown Corollary (when one horse wins the Triple Crown, the Dow drops).
“If a black cat crosses your path, it signifies that the animal is going somewhere.”
—Groucho Marx, comedian
Investment advisory services offered through Keystone Financial Services, an SEC Registered Investment Advisor. These views are those of Carson Coaching, not the presenting Representative, the Representative’s Broker/Dealer, or Registered Investment Advisor, and should not be construed as investment advice. This newsletter was prepared by Carson Coaching. Carson Coaching is not affiliated with the named firm or broker/dealer. Government bonds and Treasury Bills are guaranteed by the U.S. government as to the timely payment of principal and interest and, if held to maturity, offer a fixed rate of return and fixed principal value. However, the value of fund shares is not guaranteed and will fluctuate. Corporate bonds are considered higher risk than government bonds but normally offer a higher yield and are subject to market, interest rate and credit risk as well as additional risks based on the quality of issuer coupon rate, price, yield, maturity, and redemption features. The Standard & Poor’s 500 (S&P 500) is an unmanaged group of securities considered to be representative of the stock market in general. You cannot invest directly in this index. All indexes referenced are unmanaged. The volatility of indexes could be materially different from that of a client’s portfolio. Unmanaged index returns do not reflect fees, expenses, or sales charges. Index performance is not indicative of the performance of any investment. You cannot invest directly in an index. The Dow Jones Global ex-U.S. Index covers approximately 95% of the market capitalization of the 45 developed and emerging countries included in the Index. The 10-year Treasury Note represents debt owed by the United States Treasury to the public. Since the U.S. Government is seen as a risk-free borrower, investors use the 10-year Treasury Note as a benchmark for the long-term bond market. Gold represents the 3:00 p.m. (London time) gold price as reported by the London Bullion Market Association and is expressed in U.S. Dollars per fine troy ounce. The source for gold data is Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis (FRED), https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/GOLDPMGBD228NLBM. The Bloomberg Commodity Index is designed to be a highly liquid and diversified benchmark for the commodity futures market. The Index is composed of futures contracts on 19 physical commodities and was launched on July 14, 1998. The DJ Equity All REIT Total Return Index measures the total return performance of the equity subcategory of the Real Estate Investment Trust (REIT) industry as calculated by Dow Jones. The Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA), commonly known as “The Dow,” is an index representing 30 stock of companies maintained and reviewed by the editors of The Wall Street Journal. The NASDAQ Composite is an unmanaged index of securities traded on the NASDAQ system. International investing involves special risks such as currency fluctuation and political instability and may not be suitable for all investors. These risks are often heightened for investments in emerging markets. Yahoo! Finance is the source for any reference to the performance of an index between two specific periods. The risk of loss in trading commodities and futures can be substantial. You should therefore carefully consider whether such trading is suitable for you in light of your financial condition. The high degree of leverage is often obtainable in commodity trading and can work against you as well as for you. The use of leverage can lead to large losses as well as gains. Opinions expressed are subject to change without notice and are not intended as investment advice or to predict future performance. Economic forecasts set forth may not develop as predicted and there can be no guarantee that strategies promoted will be successful. Past performance does not guarantee future results. Investing involves risk, including loss of principal. The foregoing information has been obtained from sources considered to be reliable, but we do not guarantee it is accurate or complete. There is no guarantee a diversified portfolio will enhance overall returns or outperform a non-diversified portfolio. Diversification does not protect against market risk. Asset allocation does not ensure a profit or protect against a loss. Consult your financial professional before making any investment decision. Please contact our office if you would like a list of sources used in creating this content.
