Are we there yet?
For months, investors have wondered when the Federal Reserve (Fed) might begin to “normalize” its policies, a process that will eventually lead to higher interest rates. Last week, a better-than-expected unemployment report – showing a gain of almost a million jobs – sparked speculation about whether we’ve arrived at that point. It’s difficult to know.
When the pandemic arrived, the Fed adopted policies that stimulated growth. It cut short-term interest rates to zero and began buying Treasuries and agency mortgage-backed securities to keep long-term rates low, too. Low rates make borrowing less expensive for businesses and individuals, reported the Brookings Institute. That’s important in economically challenging times.
In late July, the Fed said it would continue to keep rates low and buy bonds until it saw “substantial further progress toward maximum employment and price stability [inflation] goals.”
The Fed may have already achieved its inflation goal. Its favorite inflation gauge is called Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE), excluding food and energy. It’s a statistic that reflects changes in how much Americans are paying for goods and services. In June, the Bureau of Economic Analysis reported that PCE was up 3.5 percent year over year. That’s well above the Fed’s two percent inflation target; however, the Fed’s new policy is to overshoot its target before raising rates.
If July’s employment numbers satisfy the Fed’s expectations for progress on jobs, the Fed may begin the process of normalizing monetary policy. The first step would be purchasing fewer bonds, a practice known as tapering. “Many market watchers are looking for [Fed Chair] Powell to discuss tapering at the central bank’s big policy meeting at Jackson Hole, Wyo., this month,” reported Randall Forsyth of Barron’s.
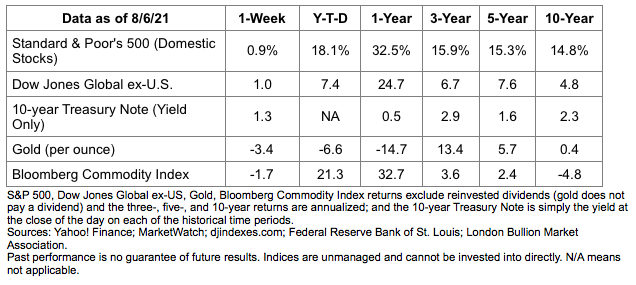
Major U.S. stock indices finished the week higher, reported Barron’s, and so did the yield on 10-year U.S. Treasuries.
What’s Making Us More Productive?
While the United States has not yet recovered all of the jobs lost during the pandemic – 22 million were lost and 16.6 million have returned – productivity is higher than it was when more people were employed.8 The Economist reported:
“Though output reached a new high in the second quarter, employment remained more than 4 percent below its pre-pandemic level… . At present, America is producing more output than it managed just a year and a half ago, with roughly 6 [million] fewer workers.”
Higher productivity undoubtedly reflects the ingenuity of American businesses. The pandemic forced companies to find ways to remain productive. In response, many adopted new technologies, implemented new patterns for working, and changed their business models.
However, not all companies have experienced gains in productivity, reported Eric Garton and Michael Mankins in the Harvard Business Review. Those that proved to be the best at managing time, talent and energy – the top 25 percent of companies – were 40 percent more productive than other companies. (The productivity of companies in the lower quartiles was averaged to make the comparison.)
Not all sectors of the economy are equally productive, either. “The surge in output per worker also reflects the changing mix of the workforce. Employment in the leisure and hospitality industries, where productivity tends to be low, remains about 10 percent below the pre-pandemic level, compared to a 3 percent shortfall in the higher-productivity manufacturing sector,” reported The Economist. As less productive sectors recover, productivity may return to previous levels.
In the meantime, some employees have been wondering whether it’s necessary to return to the workplace when productivity has been high while they’ve been working remotely. In an early July survey conducted by The Conference Board, a majority (56 percent) of employees asked whether returning to the workplace was wise, but just 18 percent of chief executive officers shared the concern.
“Whenever you are asked if you can do a job, tell ’em, ‘Certainly I can!’ Then get busy and find out how to do it.”
—Theodore Roosevelt, 26th president of the United States
Investment advisory services offered through Keystone Financial Services, an SEC Registered Investment Advisor. These views are those of Carson Coaching, not the presenting Representative, the Representative’s Broker/Dealer, or Registered Investment Advisor, and should not be construed as investment advice. This newsletter was prepared by Carson Coaching. Carson Coaching is not affiliated with the named firm or broker/dealer. Government bonds and Treasury Bills are guaranteed by the U.S. government as to the timely payment of principal and interest and, if held to maturity, offer a fixed rate of return and fixed principal value. However, the value of fund shares is not guaranteed and will fluctuate. Corporate bonds are considered higher risk than government bonds but normally offer a higher yield and are subject to market, interest rate and credit risk as well as additional risks based on the quality of issuer coupon rate, price, yield, maturity, and redemption features. The Standard & Poor’s 500 (S&P 500) is an unmanaged group of securities considered to be representative of the stock market in general. You cannot invest directly in this index. All indexes referenced are unmanaged. The volatility of indexes could be materially different from that of a client’s portfolio. Unmanaged index returns do not reflect fees, expenses, or sales charges. Index performance is not indicative of the performance of any investment. You cannot invest directly in an index. The Dow Jones Global ex-U.S. Index covers approximately 95% of the market capitalization of the 45 developed and emerging countries included in the Index. The 10-year Treasury Note represents debt owed by the United States Treasury to the public. Since the U.S. Government is seen as a risk-free borrower, investors use the 10-year Treasury Note as a benchmark for the long-term bond market. Gold represents the 3:00 p.m. (London time) gold price as reported by the London Bullion Market Association and is expressed in U.S. Dollars per fine troy ounce. The source for gold data is Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis (FRED), https://fred.stlouisfed.org/series/GOLDPMGBD228NLBM. The Bloomberg Commodity Index is designed to be a highly liquid and diversified benchmark for the commodity futures market. The Index is composed of futures contracts on 19 physical commodities and was launched on July 14, 1998. The DJ Equity All REIT Total Return Index measures the total return performance of the equity subcategory of the Real Estate Investment Trust (REIT) industry as calculated by Dow Jones. The Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA), commonly known as “The Dow,” is an index representing 30 stock of companies maintained and reviewed by the editors of The Wall Street Journal. The NASDAQ Composite is an unmanaged index of securities traded on the NASDAQ system. International investing involves special risks such as currency fluctuation and political instability and may not be suitable for all investors. These risks are often heightened for investments in emerging markets. Yahoo! Finance is the source for any reference to the performance of an index between two specific periods. The risk of loss in trading commodities and futures can be substantial. You should therefore carefully consider whether such trading is suitable for you in light of your financial condition. The high degree of leverage is often obtainable in commodity trading and can work against you as well as for you. The use of leverage can lead to large losses as well as gains. Opinions expressed are subject to change without notice and are not intended as investment advice or to predict future performance. Economic forecasts set forth may not develop as predicted and there can be no guarantee that strategies promoted will be successful. Past performance does not guarantee future results. Investing involves risk, including loss of principal. The foregoing information has been obtained from sources considered to be reliable, but we do not guarantee it is accurate or complete. There is no guarantee a diversified portfolio will enhance overall returns or outperform a non-diversified portfolio. Diversification does not protect against market risk. Asset allocation does not ensure a profit or protect against a loss. Consult your financial professional before making any investment decision. Please contact our office if you would like a list of sources used in creating this content.
